Acacia senegal (gum)
(Created page with 'Category:Schneider, A. (1921) The Microanalysis of Powdered Vegetable Drugs, 2nd ed. {{Botanical | mainimage=Microscope.png | source=Gum Arabic is the dried brit…') |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Schneider, A. (1921) The Microanalysis of Powdered Vegetable Drugs, 2nd ed.]] | [[Category:Schneider, A. (1921) The Microanalysis of Powdered Vegetable Drugs, 2nd ed.]] | ||
| − | {{Botanical | mainimage= | + | {{Botanical | mainimage=Microanalysis_powdered_vegetable_p_202_google_ver_acacia.png |
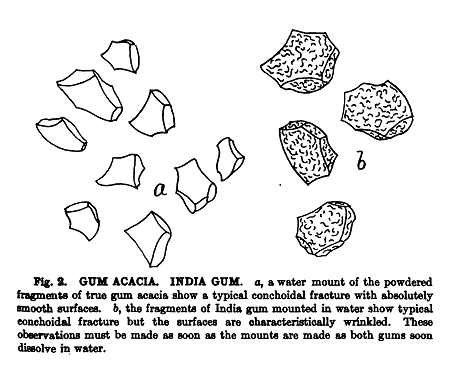
| source=Gum Arabic is the dried brittle glassy gummy exudation from Acacia senecal Willd., Mimosaceae. | | source=Gum Arabic is the dried brittle glassy gummy exudation from Acacia senecal Willd., Mimosaceae. | ||
| texture=A meal. Should not be lumpy or in sticky masses. | | texture=A meal. Should not be lumpy or in sticky masses. | ||
Revision as of 17:47, 14 January 2011
Report Description as: Common-Name (Plant-Part) (scientific name).
General Characteristics Shows no structure under the microscope. Reduce some of the gum to fine powder and dissolve about five grams in 10 parts water; centrifuge for a short time and examine the sediment for impurities which are usually present, consisting of trace of starch, some dirt and bits of vegetable tissue.
Texture A meal. Should not be lumpy or in sticky masses.
Color White to nearly snow white.
Scent Nearly odorless.
Flavor Mucilaginous taste, sticky.
Ash Content Ash should not exceed 3.6 percent.
Source: Gum Arabic is the dried brittle glassy gummy exudation from Acacia senecal Willd., Mimosaceae. [1]
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found