Angelica sinensis (root)
(addition of hptlc info.--jd) |
(addition of hptlc info.--jd) |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
=HPTLC Entries= | =HPTLC Entries= | ||
| + | {{HPTLC | source=HPTLC Association | ||
| + | | companyimage=HPTLC-assoc-Logo-farbig-Text-schwarz-300x47.png | ||
| + | | companyURL=http://www.hptlc-association.org/ | ||
| + | | mainimage=Angelica sinensis root-UV 254 nm-hptlc-association.png | ||
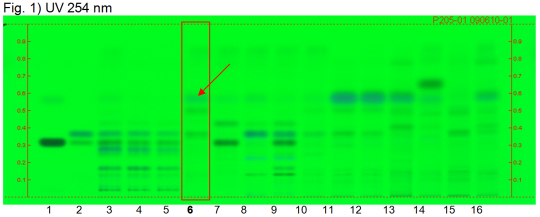
| + | | caption1=Chinese Angelica (root) HPTLC ID - UV 254 nm | ||
| + | | description=Chinese Angelica (root) (''Angelica sinensis'') | ||
| + | | image2=Angelica sinensis root-UV 366 nm-hptlc-association.png | ||
| + | | caption2=Chinese Angelica (root) HPTLC ID - UV 366 nm | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | stationaryphase=Stationary phase, i.e. Silica gel 60, F254 | ||
| + | | mobilephase= Toluene, ethyl acetate, glacial acetic acid 90:10:1 (v/v/v) | ||
| + | | prep=Sample: Mix 1.0 g of powdered sample with 4 mL of heptane and sonicate for 5 minutes, then centrifuge and filter the solutions and use the filtrates as test solutions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | | detection=Saturated chamber; developing distance 70 mm from lower edge; relative humidity 33% | ||
| + | | referencesamples=Reference:Dissolve 1 mg each of osthole and imperatorin in 10 mL of methanol. Optional: Dissolve 1 mg of Z-ligustilide in 10 mL of methanol. | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | lanes=Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample): | ||
| + | # 4 µL Imperatorin, z-Ligustilide (incr. Rf) | ||
| + | # 4 µL Osthole | ||
| + | # 4 µL Angelica root 1* | ||
| + | # 4 µL Angelica root 2 | ||
| + | # 4 µL Angelica root 3 | ||
| + | # '''4 µL Chinese Angelica root''' | ||
| + | # 4 µL Dahurian Angelica root | ||
| + | # 4 µL Doubleteeth pubescent Angelica root 1 | ||
| + | # 4 µL Doubleteeth pubescent Angelica root 2 | ||
| + | # 4 µL Lovage root 1* | ||
| + | # 4 µL Lovage root 2 | ||
| + | # 4 µL Lovage root 3 | ||
| + | # 4 µL Chinese lovage root (Ligusticum sinensis) | ||
| + | # 4 µL Chinese lovage root 1 (Ligusticum jeholense) | ||
| + | # 4 µL Chinese lovage root 2 (Ligusticum jeholense) | ||
| + | # 4 µL Chinese lovage root (Ligusticum chuanxiong) | ||
| + | |||
| + | | notes=''Images presented in this entry are examples and are not intended to be used as basis for setting specifications for quality control purposes.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | System suitability test: Imperatorin: greenish fluorescent zone at Rf ~ 0.31 (UV 366 nm). Osthole: blue fluorescent zone at Rf ~ 0.36 (UV 366 nm). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Identification: Compare result with reference images. The fingerprint of the test solution is similar to that of the corresponding botanical reference sample. Additional weak zones may be present. Under UV 254 nm the chromatogram of the test solution shows a blue fluorescent zone corresponding to reference Z-ligustilide (red arrow). Below this zone there are two weak quenching zones, one of them at the position corresponding to osthole. Under UV 366 nm the chromatogram of the test solution shows an intense blue white fluorescent zone corresponding to reference Z-ligustilide. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Test for adulteration: Under UV 254 nm no zone is seen at or below the position of imperatorin. Under UV 366 nm no zone is seen at or below the position of osthole (Angelica root, Dahurian Angelica root, Doubleteeth pubescent root, Lovage root, Chinese lovage root. | ||
| + | |||
| + | | }} | ||
{{HPTLC | source=HPTLC Association | {{HPTLC | source=HPTLC Association | ||
| companyimage=HPTLC-assoc-Logo-farbig-Text-schwarz-300x47.png | | companyimage=HPTLC-assoc-Logo-farbig-Text-schwarz-300x47.png | ||
Revision as of 18:21, 21 June 2013
Contents |
Introduction
Introduction from Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angelica_sinensis, retrieved 02/20/2012).
Angelica sinensis, commonly known as "dong quai" or "female ginseng" is a herb from the family Apiaceae, indigenous to China.
Its dried root is commonly known in Chinese as Radix Angelicae Sinensis, or Chinese angelica (simplified Chinese: 当归; traditional Chinese: 當歸; pinyin: dāngguī; Pe̍h-ōe-jī: tong-kui) and is widely used in Chinese traditional medicine to treat gynecological ailments, fatigue, mild anemia and high blood pressure. It has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic and sedative effects. The plant's phytochemicals consist of coumarins, phytosterols, polysaccharides, ferulate, and flavonoids. It has antioxidant activity.
The quoted text in this section was licensed for use under the Creative Commons ShareAlike License, version 3.0: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Macroscopic Entries
Microscopic Entries
|
HPTLC Entries
|
Chinese Angelica (root) (Angelica sinensis) Lane Assignments Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample):
Reference Sample(s) Reference:Dissolve 1 mg each of osthole and imperatorin in 10 mL of methanol. Optional: Dissolve 1 mg of Z-ligustilide in 10 mL of methanol. Stationary Phase Stationary phase, i.e. Silica gel 60, F254 Mobile Phase Toluene, ethyl acetate, glacial acetic acid 90:10:1 (v/v/v) Sample Preparation Method Sample: Mix 1.0 g of powdered sample with 4 mL of heptane and sonicate for 5 minutes, then centrifuge and filter the solutions and use the filtrates as test solutions. Detection Method Saturated chamber; developing distance 70 mm from lower edge; relative humidity 33% Other Notes Images presented in this entry are examples and are not intended to be used as basis for setting specifications for quality control purposes. System suitability test: Imperatorin: greenish fluorescent zone at Rf ~ 0.31 (UV 366 nm). Osthole: blue fluorescent zone at Rf ~ 0.36 (UV 366 nm). Identification: Compare result with reference images. The fingerprint of the test solution is similar to that of the corresponding botanical reference sample. Additional weak zones may be present. Under UV 254 nm the chromatogram of the test solution shows a blue fluorescent zone corresponding to reference Z-ligustilide (red arrow). Below this zone there are two weak quenching zones, one of them at the position corresponding to osthole. Under UV 366 nm the chromatogram of the test solution shows an intense blue white fluorescent zone corresponding to reference Z-ligustilide. Test for adulteration: Under UV 254 nm no zone is seen at or below the position of imperatorin. Under UV 366 nm no zone is seen at or below the position of osthole (Angelica root, Dahurian Angelica root, Doubleteeth pubescent root, Lovage root, Chinese lovage root. Source: HPTLC Association [2] |
|
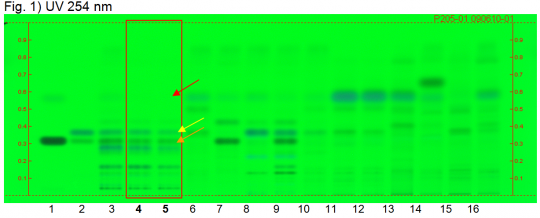
Angelica (root) (Angelica archangelica) Lane Assignments Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample):
Reference Sample(s) Reference: Dissolve 1 mg each of osthole and imperatorin in 10 mL of methanol. Optional: Dissolve 1 mg of Z-ligustilide in 10 mL of methanol. Stationary Phase Stationary phase, i.e. Silica gel 60, F254 Mobile Phase Toluene, ethyl acetate, glacial acetic acid 90:10:1 (v/v/v) Sample Preparation Method Sample: Mix 1.0 g of powdered sample with 4 mL of heptane and sonicate for 5 minutes, then centrifuge and filter the solutions and use the filtrates as test solutions. Detection Method Saturated chamber; developing distance 70 mm from lower edge; relative humidity 33% Other Notes Images presented in this entry are examples and are not intended to be used as basis for setting specifications for quality control purposes. System suitability test: Imperatorin: greenish fluorescent zone at Rf ~ 0.31 (UV 366 nm). Osthole: blue fluorescent zone at Rf ~ 0.36 (UV 366 nm). Identification: Compare result with reference images. Under UV 254 nm the chromatogram of the test solution shows quenching zones corresponding to references imperatorin and osthole (Rf ~ 0.31 and Rf ~ 0.36, orange and yellow arrow). Below these zones several quenching zones are detected. Under UV 366 nm the chromatogram of the test solution shows a dark blue fluorescent zone corresponding to the reference osthole. Right below a greenish fluorescent zone corresponding to imperatorin is detected. Below this zone several blue fluorescent zones are detected. Test for adulteration: No zone is seen at or directly below Rf ~ 0.57 (red arrow) (Chinese Angelica root, Dahurian Angelica root, Doubleteeth pubescent root, Lovage root, Chinese lovage root). Source: HPTLC Association [3] |
Other Points of Interest
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found