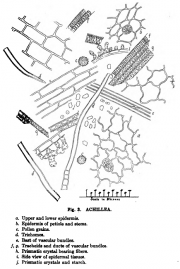
Achillea millefolium (flower)
(→fix HPTLC samples) |
|||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
Derivatization reagent: Anisaldehyde reagent; Preparation: 170 mL of ice cooled methanol are mixed with 20 mL of acetic acid, 10 mL of sulfuric acid, and 1 mL of anisaldehyde. Use: Dip (time 0, speed 5), heat at 100°C for 4 min. | Derivatization reagent: Anisaldehyde reagent; Preparation: 170 mL of ice cooled methanol are mixed with 20 mL of acetic acid, 10 mL of sulfuric acid, and 1 mL of anisaldehyde. Use: Dip (time 0, speed 5), heat at 100°C for 4 min. | ||
| detection=Saturated chamber; developing distance 70 mm from lower edge; relative humidity 33% | | detection=Saturated chamber; developing distance 70 mm from lower edge; relative humidity 33% | ||
| − | | | + | | referencesamples=Reference: Dissolve 25 mg of cineole in 20 mL of tolulene. Dissolve 10 mg of guaiazulene in 20 mL of tolulene. |
| | | | ||
| lanes= Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample): | | lanes= Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample): | ||
Revision as of 13:33, 16 October 2012
Contents |
Introduction
Introduction from Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Achillea_millefolium, retrieved 02/20/2012).
Achillea millefolium or yarrow is a flowering plant in the family Asteraceae, native to the Northern Hemisphere. In New Mexico and southern Colorado, it is called plumajillo, or "little feather", for the shape of the leaves. In antiquity, yarrow was known as herbal militaris, for its use in staunching the flow of blood from wounds. Other common names for this species include common yarrow, gordaldo, nosebleed plant, old man's pepper, devil's nettle, sanguinary, milfoil, soldier's woundwort, thousand-leaf (as its binomial name affirms), and thousand-seal.
Common yarrow is an erect herbaceous perennial plant that produces one to several stems (0.2 to 1m tall) and has a rhizomatous growth form. Leaves are evenly distributed along the stem, with the leaves near the middle and bottom of the stem being the largest. The leaves have varying degrees of hairiness (pubescence). The leaves are 5–20 cm long, bipinnate or tripinnate, almost feathery, and arranged spirally on the stems. The leaves are cauline and more or less clasping. The inflorescence has 4 to 9 phyllaries and contains ray and disk flowers which are white to pink. There are generally 3 to 8 ray flowers that are ovate to round. Disk flowers range from 15 to 40. The inflorescence is produced in a flat-topped cluster. The fruits are small achenes. Yarrow grows at low or high altitudes, up to 3500m above sea level. The plant commonly flowers from May through June, and is a frequent component in butterfly gardens. Common yarrow is frequently found in the mildly disturbed soil of grasslands and open forests. Active growth occurs in the spring.
In North America, there are both native and introduced genotypes, and both diploid and polyploid plants. The plant has a strong, sweet scent, similar to chrysanthemums.
The quoted text in this section was licensed for use under the Creative Commons ShareAlike License, version 3.0: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Macroscopic Entries
|
Microscopic Entries
|
|
HPTLC Entries
|
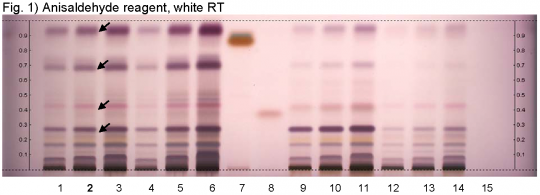
Yarrow (flower) (Achillea millefolium) Lane Assignments Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample):
Reference Sample(s) Reference: Dissolve 25 mg of cineole in 20 mL of tolulene. Dissolve 10 mg of guaiazulene in 20 mL of tolulene. Stationary Phase Stationary phase, i.e. Silica gel 60, F254 Mobile Phase Tolulene, ethyl acetate 95:5 (v/v) Sample Preparation Method Sample: Mix 1.0 g of powdered sample with 10 mL of methanol and sonicate for 10 minutes, then centrifuge or filter the solutions and use the supernatants / filtrates as test solutions. Derivatization reagent: Anisaldehyde reagent; Preparation: 170 mL of ice cooled methanol are mixed with 20 mL of acetic acid, 10 mL of sulfuric acid, and 1 mL of anisaldehyde. Use: Dip (time 0, speed 5), heat at 100°C for 4 min. Detection Method Saturated chamber; developing distance 70 mm from lower edge; relative humidity 33% Other Notes Images presented in this entry are examples and are not intended to be used as a bases for setting specifications for quality control purposes. System suitability test: Cineole: violet zone at Rf ~ 0.38. Guaiazulene: brown zone at Rf ~ 0.88. Application: 2 μL of references, 16 μL of test solutions Identification: Compare result with reference images. The fingerprint of the test solution is similar to that of the corresponding botanical reference sample. Additional weak zones may be present. The chromatogram of the test solution shows a violet zone at Rf ~ 0.94 right above the zone due to guaiazulene reference substance. Below this zone there is a violet zone at Rf ~ 0.70. There is a reddish-violet zone at Rf ~ 0.43 right above the zone due to cineole reference substance. Below this zone there is a violet zone at Rf ~ 0.29 (black arrows).
|
Other Points of Interest
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found