Aesculus hippocastanum (seed)
(add askbox) |
(Botanical Voucher Kew added) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
|notes=}} | |notes=}} | ||
=Botanical Voucher Specimen= | =Botanical Voucher Specimen= | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{Media2 |cat=Voucher |
| companyimage=AP-LOGO-Laboratories Crop - Copy.jpg | | companyimage=AP-LOGO-Laboratories Crop - Copy.jpg | ||
| companyURL=http://www.alkemist.com | | companyURL=http://www.alkemist.com | ||
|mainimage=Aesculus hippocastanum MF32004BMX1 A1299.jpg | |mainimage=Aesculus hippocastanum MF32004BMX1 A1299.jpg | ||
| − | |source=Botanical Voucher Specimen Library, Alkemists Laboratories}} | + | |source=Botanical Voucher Specimen Library, Alkemists Laboratories |
| + | | companyimage2=Kewlogo.gif | ||
| + | | companyURL2=http://specimens.kew.org/herbarium/K000914265 | ||
| + | | image2=Aesculus_hippocastanum_Kew_imageBarcode=K000914265_517072.jpg | ||
| + | | source2=Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. | ||
| + | |||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
=Organoleptic Characteristics= | =Organoleptic Characteristics= | ||
Revision as of 22:15, 18 August 2014
Contents |
Nomenclature
Aesculus hippocastanum L. Hippocastanaceae
Standardized common name (English): horse chestnut
Botanical Voucher Specimen
 |
 |
|
|
|
Organoleptic Characteristics
|
Macroscopic Characteristics
|
|
|
|
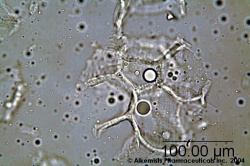
Microscopic Characteristics
 |
 |
|
|
|
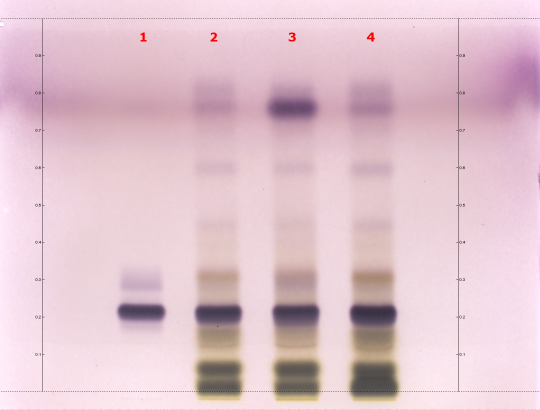
High Performance Thin Layer Chromatographic Identification
|
Horse Chestnut (seed) (Aesculus hippocastanum) Lane Assignments Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample):
Reference Sample(s) Reference: Dissolve 15 mg of escin in 3 mL of methanol. Stationary Phase Stationary phase, i.e. Silica gel 60, F254 Mobile Phase 1-butanol, water, glacial acetic acid 50:40:10 (v/v/v) Sample Preparation Method Sample: Mix 1 g of powdered sample with 10 mL of ethanol-water (7:3), heat on a steam bath for 10 minutes, then centrifuge or filter the solutions and use the supernatants / filtrates as test solutions Anisaldehyde Reagent Preparation: 1mL anisaldehyde reagent, 20mL acetic acid 99%, 170mL methanol, 10ml sulfuric acid 95%-97% Detection Method Anisaldehyde Reagent Use: Dip (time 0, speed 5), heat at 100°C for 4 min Other Notes Compare result under white RT with reference images in Image Comparison Viewer. The fingerprint of the test solution is similar to that of the corresponding botanical reference sample. Additional weak zones may be present. A. hippocastanum Identification: Above the zone due to escin the chromatogram shows several narrow, brown to brownish-red zones that are less intense than the zone corresponding to escin.
|
Supplementary Information
Sources
- ↑ Botanical Voucher Specimen Library, Alkemists Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. http://specimens.kew.org/herbarium/K000914265
- ↑ United States Dispensatory (1918)
- ↑ Tropicos.org. Missouri Botanical Garden. 05 Aug 2013 http://www.tropicos.org/Image/35153
- ↑ PlantaPhile http://plantaphile.com/
- ↑ PlantaPhile http://plantaphile.com/
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ CAMAG HPTLC http://www.camag.com/index.php
- Botanical
- Hippocastanaceae
- Media
- Voucher
- Botanical Voucher Specimen Library, Alkemists Laboratories
- Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
- Organolepsy
- United States Dispensatory (1918)
- Macroscopy
- Tropicos.org. Missouri Botanical Garden. 05 Aug 2013
- PlantaPhile
- Microscopy
- Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories
- HPTLC
- CAMAG HPTLC