Chamaemelum nobile (flower)
m (moved Anthemis nobilis (flowers) to Chamaemelum nobile (flower): GRIN name update) |
(addition of hptlc info.--jd) |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
| }} | | }} | ||
=HPTLC Entries= | =HPTLC Entries= | ||
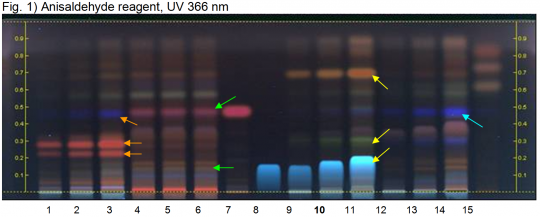
| + | {{HPTLC | source=HPTLC Association | ||
| + | | companyimage=HPTLC-assoc-Logo-farbig-Text-schwarz-300x47.png | ||
| + | | companyURL=http://www.hptlc-association.org/ | ||
| + | | mainimage=Chamaemelum nobile-Anisaldehyde reagent, UV 366 nm-hptlc-association.png | ||
| + | | caption1=Roman chamomile (flower) HPTLC ID - Anisaldehyde reagent, UV 366 nm | ||
| + | | description=Roman chamomile (flower) (''Chamaemelum nobile'') | ||
| + | | image2=Chamaemelum nobile-Anisaldeyhde reagent, white RT-hptlc-association.png | ||
| + | | caption2=Roman chamomile (flower) HPTLC ID - Anisaldeyhde reagent, white RT | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | stationaryphase=Stationary phase, i.e. Silica gel 60, F254 | ||
| + | | mobilephase=Ethyl acetate, cyclohexane 1:1 (v/v) | ||
| + | | prep=Sample:Mix 1 g of powdered sample with 10 mL of methanol and sonicate for 10 minutes, then centrifuge or filter the solutions and use the supernatants / filtrates as test solutions. Dissolve 10 µL of the essential oil in 1 mL of toluene. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Derivatization reagent: Anisaldehyde reagent; Preparation: 170 mL of ice-cooled methanol are mixed with 20 mL of acetic acid, 10 mL of sulfuric acid and 1 mL of anisaldehyde; Use: Dip (time 0, speed 5), heat at 100°C for 4 min. | ||
| + | | detection=Saturated chamber; developing distance 70 mm from lower edge; relative humidity 33% | ||
| + | | referencesamples=Reference: Dissolve 1.5 mg of apigenin in 5 mL of methanol. Dissolve 1 mg of parthenolide in 5 mL of methanol. | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | lanes=Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample): | ||
| + | # 1 µL Feverfew flower from Mexico | ||
| + | # 2 µL Feverfew flower from Mexico | ||
| + | # 4 µL Feverfew flower from Mexico | ||
| + | # 3 µL Feverfew flower | ||
| + | # 3.5 µL Feverfew flower | ||
| + | # 4 µL Feverfew flower | ||
| + | # 2 µL Parthenolide | ||
| + | # 2 µL Apigenin | ||
| + | # 1 µL Roman Chamomile flower | ||
| + | # '''2 µL Roman Chamomile flower''' | ||
| + | # 4 µL Roman Chamomile flower | ||
| + | # 1 µL Matricaria flower | ||
| + | # 2 µL Matricaria flower | ||
| + | # 4 µL Matricaria flower | ||
| + | # 1 µL Matricaria flower oil | ||
| + | |||
| + | | notes=''Images presented in this entry are examples and are not intended to be used as basis for setting specifications for quality control purposes.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | System suitability test (UV 366 nm): Apigenin: blue zone at Rf ~ 0.20; Parthenolide: pink zone at Rf ~ 0.48 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Identification: Compare result with reference images. The fingerprint of the test solution is similar to that of the corresponding botanical reference sample. Additional weak zones may be present. Under UV 366 nm the chromatogram of the test solution shows a strongly tailing blue zone at the position of reference substance apigenin at Rf ~ 0.20. There is a characteristic greenish zone (red zone under white light) at Rf ~ 0.30 and an intense orange zone (violet zone under white light) at Rf ~ 0.7 (yellow arrows). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Test for adulteration: Under UV 366 nm there are no intense red zones (violet zone under white light) between Rf ~ 0.20 and 0.30. No blue zone is seen at the position of parthenolide (orange arrows; Feverfew flower from Mexico). Under UV 366 nm no pink zone (violet zone under white light) at Rf ~ 0.48 corresponding to reference substance parthenolide is seen and there are no brown zones at the position of apigenin at Rf ~ 0.20 (green arrows, Feverfew flower). Under UV 366 nm no blue zone is seen at the position of parthenolide (blue arrow; Chamomile flower). Chamomile flower oil does not show any zones below Rf ~ 0.60. | ||
| + | | }} | ||
=Other Points of Interest= | =Other Points of Interest= | ||
Revision as of 18:51, 21 June 2013
Contents |
Introduction
Introduction from Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anthemis_nobilis, retrieved 02/20/2012).
Chamaemelum nobile, commonly known as Roman camomile, chamomile, garden camomile, ground apple, low chamomile, English chamomile, or whig plant, is a low perennial plant found in dry fields and around gardens and cultivated grounds. It has daisy-like white flowers that are found in Europe, North America, and Argentina. The stem is procumbent, the leaves alternate, bipinnate, finely dissected, and downy to glabrous. The solitary, terminal flowerheads, rising 8 to twelve inches above the ground, consist of prominent yellow disk flowers and silver-white ray flowers. The flowering time is June and July, and its fragrance is sweet, crisp, fruity and herbaceous.
The plant is used to flavor foods, in tisanes, perfumes, and cosmetics. It is used to make a rinse for blonde hair, and is popular in aromatherapy, whose practitioners believe it to be a calming agent to end stress and aid in sleep.
The word chamomile comes from Greek χαμαίμηλον (chamaimēlon), "earth-apple", from χαμαί (chamai), "on the ground" + μήλον (mēlon), "apple", so called because of the applelike scent of the plant. (Note: The "ch-" spelling is used especially in science and pharmacology.)
The quoted text in this section was licensed for use under the Creative Commons ShareAlike License, version 3.0: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Macroscopic Entries
Microscopic Entries
|
HPTLC Entries
|
Roman chamomile (flower) (Chamaemelum nobile) Lane Assignments Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample):
Reference Sample(s) Reference: Dissolve 1.5 mg of apigenin in 5 mL of methanol. Dissolve 1 mg of parthenolide in 5 mL of methanol. Stationary Phase Stationary phase, i.e. Silica gel 60, F254 Mobile Phase Ethyl acetate, cyclohexane 1:1 (v/v) Sample Preparation Method Sample:Mix 1 g of powdered sample with 10 mL of methanol and sonicate for 10 minutes, then centrifuge or filter the solutions and use the supernatants / filtrates as test solutions. Dissolve 10 µL of the essential oil in 1 mL of toluene. Derivatization reagent: Anisaldehyde reagent; Preparation: 170 mL of ice-cooled methanol are mixed with 20 mL of acetic acid, 10 mL of sulfuric acid and 1 mL of anisaldehyde; Use: Dip (time 0, speed 5), heat at 100°C for 4 min. Detection Method Saturated chamber; developing distance 70 mm from lower edge; relative humidity 33% Other Notes Images presented in this entry are examples and are not intended to be used as basis for setting specifications for quality control purposes. System suitability test (UV 366 nm): Apigenin: blue zone at Rf ~ 0.20; Parthenolide: pink zone at Rf ~ 0.48 Identification: Compare result with reference images. The fingerprint of the test solution is similar to that of the corresponding botanical reference sample. Additional weak zones may be present. Under UV 366 nm the chromatogram of the test solution shows a strongly tailing blue zone at the position of reference substance apigenin at Rf ~ 0.20. There is a characteristic greenish zone (red zone under white light) at Rf ~ 0.30 and an intense orange zone (violet zone under white light) at Rf ~ 0.7 (yellow arrows). Test for adulteration: Under UV 366 nm there are no intense red zones (violet zone under white light) between Rf ~ 0.20 and 0.30. No blue zone is seen at the position of parthenolide (orange arrows; Feverfew flower from Mexico). Under UV 366 nm no pink zone (violet zone under white light) at Rf ~ 0.48 corresponding to reference substance parthenolide is seen and there are no brown zones at the position of apigenin at Rf ~ 0.20 (green arrows, Feverfew flower). Under UV 366 nm no blue zone is seen at the position of parthenolide (blue arrow; Chamomile flower). Chamomile flower oil does not show any zones below Rf ~ 0.60. Source: HPTLC Association [2] |
Other Points of Interest
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found