From AHPA Botanical Identity References Compendium
(Difference between revisions)
|
|
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | + | {{DISPLAYTITLE:''Garcinia hanburyi'' (gum resin) }} |
| | =Nomenclature= | | =Nomenclature= |
| | | | |
| Line 11: |
Line 12: |
| | |notes=The gum resin of G. hanburyi is also commonly called gamboge. }} | | |notes=The gum resin of G. hanburyi is also commonly called gamboge. }} |
| | | | |
| − | =Macroscopic Entries= | + | =Botanical Voucher Specimen= |
| | + | =Organoleptic Characteristics= |
| | + | |
| | + | =Macroscopic Characteristics= |
| | {{Macroscopy | source=United States Dispensatory (1918) | | {{Macroscopy | source=United States Dispensatory (1918) |
| | | description=The official description is [in part] as follows: | | | description=The official description is [in part] as follows: |
| Line 19: |
Line 23: |
| | }} | | }} |
| | | | |
| − | =Microscopic Entries= | + | =Microscopic Characteristics= |
| | {{Macroscopy | source=United States Dispensatory (1918) | | {{Macroscopy | source=United States Dispensatory (1918) |
| | | description=The official description is [in part] as follows: | | | description=The official description is [in part] as follows: |
| Line 37: |
Line 41: |
| | | }} | | | }} |
| | | | |
| − | =HPTLC Entries= | + | =High Performance Thin Layer Chromatographic Identification= |
| | | | |
| − | =Other Points of Interest= | + | =Supplementary Information= |
| | + | =Sources= |
| | + | <references /> |
Revision as of 23:43, 15 March 2014
Nomenclature
Garcinia hanburyi Hook. f. Clusiaceae
Syn. Hanbury's garcinia; Siam gamboge
Standardized common name (English): gamboge
Botanical Voucher Specimen
Organoleptic Characteristics
Macroscopic Characteristics
| The official description is [in part] as follows:
"In hard, brittle, cylindrical pieces, usually hollow in the center, from 2 to 5 cm. in diameter, from 10 to 20 cm in length, externally grayish-orange-brown, longitudinally striate; fracture conchoidal, smooth, orange-red: odorless; taste very acrid. When rubbed with water it yields a yellow emulsion which becomes darker and almost transparent upon the addition of ammonia water. The emulsion turns green upon the addition of iodine T.S. (starch)." U.S.
It has no odor, and little taste, but, after remaining a short time in the mouth, produces an acrid sensation in the fauces.
Source: United States Dispensatory (1918) [1]
|
|
|
|
Microscopic Characteristics
| The official description is [in part] as follows:
"The powder is bright yellow, containing few or no starch grains. When mounted in hydrated chloral T.S. and examined under the microscope the particles, for the most part, slowly dissolve, leaving scattered fragments of vegetable tissues. Not less than 65 per cent. of Gamboge is soluble in alcohol." U.S.
Source: United States Dispensatory (1918) [2]
|
|
|
|
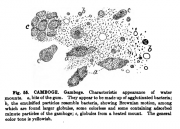
| Cambodia (gum resin) (Garcinia hanburii) H. Guttiferae.The microscope reveals little that is characteristic. Fragments of vegetable tissue are sparingly present. There is no starch present. The emulsified particles resemble bacteria and show active Brownian movement.
Source: Schneider, A. (1921) The Microanalysis of Powdered Vegetable Drugs, 2nd ed. [3]
|
|
|
|
High Performance Thin Layer Chromatographic Identification
Supplementary Information
Sources
- ↑ United States Dispensatory (1918)
- ↑ United States Dispensatory (1918)
- ↑ Schneider, A. (1921) The Microanalysis of Powdered Vegetable Drugs, 2nd ed.