Magnolia officinalis (bark)
(Nomenclature updated) |
(add Kew voucher specimen reference) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{DISPLAYTITLE:''Magnolia officinalis'' (bark) }} {{askbox|herb=''Magnolia officinalis''}} | ||
=Nomenclature= | =Nomenclature= | ||
| Line 11: | Line 12: | ||
|notes=See note following M. biondii. }} | |notes=See note following M. biondii. }} | ||
| − | =Macroscopic | + | =Botanical Voucher Specimen= |
| − | =Microscopic | + | {{Media |cat=Voucher |
| − | {{Microscopy | source=Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories | + | | companyimage=Kewlogo.gif |
| + | | companyURL=http://specimens.kew.org/herbarium/K000681415 | ||
| + | | mainimage=Magnolia officinalis Kew barcode=K000681415 308529.jpg | ||
| + | | source=Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | =Organoleptic Characteristics= | ||
| + | {| border=1 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | {{Organolepsy | source=United States Dispensatory (1918) | ||
| + | | description=[The bark of ''Magnolia officinalis'' is] inodorous; taste somewhat astringent, pungent, and bitter. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The aromatic property, which resides in a volatile principle, is diminished by desiccation, and entirely lost when the bark is long kept. The bitterness, however, remains. The bark is destitute of astringency.}} | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | =Macroscopic Characteristics= | ||
| + | {| border=1 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | {{Macroscopy | source=United States Dispensatory (1918) | ||
| + | | description=The bark from young wood is quilled or curved, thin, externally orange-brown and glossy, or light gray, with scattered warts and somewhat fissured, internally whitish or pale brownish and smooth; fracture short, in the inner layer somewhat fibrous ... | ||
| + | |||
| + | The bark of old wood, deprived of the cork, is whitish or brownish, fibrous, and less pungent.}} | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Microscopic Characteristics= | ||
| + | {{Media3 |cat=Microscopy | source=Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories | ||
| companyimage= AP-LOGO-Laboratories Crop - Copy.jpg | | companyimage= AP-LOGO-Laboratories Crop - Copy.jpg | ||
| − | | companyURL=http://www. | + | | companyURL=http://www.alkemist.com |
| mainimage=Magnolia_officinalis_-_Alkemist_Laboratories.jpg | | mainimage=Magnolia_officinalis_-_Alkemist_Laboratories.jpg | ||
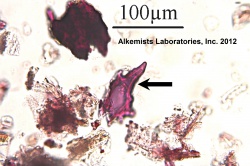
| caption1=Cells containing yellow-brown oil observed at 400x with Acidified Chloral Hydrate Glycerol Solution. | | caption1=Cells containing yellow-brown oil observed at 400x with Acidified Chloral Hydrate Glycerol Solution. | ||
| − | | | + | | source2=Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories |
| + | | companyimage2= AP-LOGO-Laboratories Crop - Copy.jpg | ||
| + | | companyURL2=http://www.alkemist.com | ||
| image2=Magnolia_officinalis-2_-_Alkemist_Laboratories.jpg | | image2=Magnolia_officinalis-2_-_Alkemist_Laboratories.jpg | ||
| caption2=Star shaped lignified sclereids observed at 400x with phloroglucinol + HCl. | | caption2=Star shaped lignified sclereids observed at 400x with phloroglucinol + HCl. | ||
| + | | source3=Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories | ||
| + | | companyimage3= AP-LOGO-Laboratories Crop - Copy.jpg | ||
| + | | companyURL3=http://www.alkemist.com | ||
| image3=Magnolia_officinalis-3_-_Alkemist_Laboratories.jpg | | image3=Magnolia_officinalis-3_-_Alkemist_Laboratories.jpg | ||
| caption3=Lignified fibers observed at 400x with phloroglucinol + HCl. | | caption3=Lignified fibers observed at 400x with phloroglucinol + HCl. | ||
| Line 26: | Line 55: | ||
| }} | | }} | ||
| − | = | + | =High Performance Thin Layer Chromatographic Identification= |
{{HPTLC | source=Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories | {{HPTLC | source=Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories | ||
| description=Magnolia (bark) (''Magnolia officinalis'') | | description=Magnolia (bark) (''Magnolia officinalis'') | ||
| Line 52: | Line 81: | ||
| }} | | }} | ||
| − | = | + | =Supplementary Information= |
| − | + | =Sources= | |
| + | <references /> | ||
Latest revision as of 14:52, 26 May 2015
Contents |
Nomenclature
Magnolia officinalis Rehder & E.H. Wilson Magnoliaceae
Standardized common name (English): magnolia
Pinyin name(s): hou po; hou po (bark of stem; twig; and root); hou po hua (flower bud)
Botanical Voucher Specimen
 |
|
|
Organoleptic Characteristics
|
Macroscopic Characteristics
|
Microscopic Characteristics
 |
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
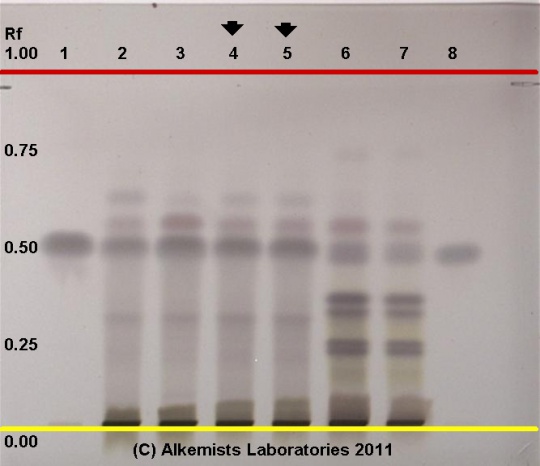
High Performance Thin Layer Chromatographic Identification
|
Magnolia (bark) (Magnolia officinalis) Lane Assignments Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample):
Reference materials used here have been authenticated by macroscopic, microscopic &/or TLC studies according to the reference source cited below held at Alkemists Laboratories, Costa Mesa, CA. Stationary Phase Silica gel 60, F254, 10 x 10 cm HPTLC plates Mobile Phase cyclohexane: ethyl acetate: HCOOH [6/4/0.2] Sample Preparation Method 0.3g+3mL 70% grain EtOH sonicate/heat @~50° C ~ 1/2 hr Detection Method 10% Ethanolic H2SO4 -> 115° C 15 min -> visible light Reference see Pharmacopoeia of The Peoples Republic of China, Volume 1, 1997
|
Supplementary Information
Sources
- ↑ Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. http://specimens.kew.org/herbarium/K000681415
- ↑ United States Dispensatory (1918)
- ↑ United States Dispensatory (1918)
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com