Panax quinquefolius (root)
From AHPA Botanical Identity References Compendium
(Difference between revisions)
(add askbox) |
(add USD 1918 information (organoleptic and macroscopic)) |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
=Organoleptic Characteristics= | =Organoleptic Characteristics= | ||
| + | {| border=1 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | {{Organolepsy | source=United States Dispensatory (1918) | ||
| + | | description=[''Panax ginseng'' (root)] has a feeble odor, and a sweet, slightly aromatic taste, somewhat analogous to that of licorice root.}} | ||
| + | |} | ||
=Macroscopic Characteristics= | =Macroscopic Characteristics= | ||
| + | {| border=1 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | {{Macroscopy | source=United States Dispensatory (1918) | ||
| + | | description=The root is fleshy, somewhat spindle-shaped, from 5 to 12 cm. long, and 1 to 2.5 cm. thick, and terminated by one or more stem scars. Frequently there are two portions, sometimes three or more, connected at their upper extremity, and bearing a supposed, though very remote, resemblance to the human figure, from which circumstance it is said that the Chinese name ginseng originated. When dried, the root is yellowish-white and wrinkled externally, and within consists usually of a hard central portion, surrounded by a soft whitish bark. }} | ||
| + | |} | ||
=Microscopic Characteristics= | =Microscopic Characteristics= | ||
Revision as of 19:46, 31 March 2015
Contents |
Nomenclature
Panax quinquefolius L. Araliaceae
Standardized common name (English): American ginseng
Pinyin name(s): xi yang shen (root)
Botanical Voucher Specimen
|
|
Organoleptic Characteristics
|
Macroscopic Characteristics
|
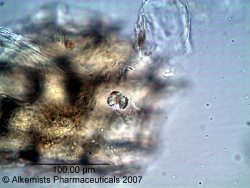
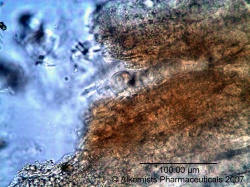
Microscopic Characteristics
 |
 |
|
|
|
High Performance Thin Layer Chromatographic Identification
Supplementary Information
Sources
- ↑ MOBOT, Tropicos.org http://www.tropicos.org/Image/53111
- ↑ United States Dispensatory (1918)
- ↑ United States Dispensatory (1918)
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com