Rosa canina (fruit)
(add USD 1918 information (organoleptic and macroscopic)) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | = | + | {{DISPLAYTITLE:''Rosa canina'' (fruit) }} {{askbox|herb=''Rosa canina''}} |
| − | = | + | =Nomenclature= |
| − | = | + | {{nomenclature | binomial=Rosa canina |
| + | |authority=L. | ||
| + | |family=Rosaceae | ||
| + | |scn=dog rose | ||
| + | |syn= | ||
| + | |ayurvedic= | ||
| + | |pinyin= | ||
| + | |aka=dog brier; brier rose | ||
| + | |notes=This species of Rosa is a primary source of rose hips. The use of this common name for the plant's fruit is well established and is an acceptable and even preferable standard common name. }} | ||
| − | {{Microscopy | source=Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories | + | =Botanical Voucher Specimen= |
| + | |||
| + | {{Media |cat=Voucher | ||
| + | |||
| + | | source=MOBOT, Tropicos.org | ||
| + | | mainimage=Rosa_canina_Tropicos_100179847_(S).jpg | ||
| + | | companyimage=TropicosLogo.gif | ||
| + | | companyURL=http://www.tropicos.org/Image/100179847 | ||
| + | | reference=Tropicos.org. Missouri Botanical Garden. 26 Mar 2014 <http://www.tropicos.org/Image/100179847> | ||
| + | |||
| + | | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Organoleptic Characteristics= | ||
| + | {| border=1 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | {{Organolepsy | source=United States Dispensatory (1918) | ||
| + | | description=Rose hips possess a pleasant, sweet, acidulous taste. }} | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Macroscopic Characteristics= | ||
| + | {| border=1 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | {{Macroscopy | source=United States Dispensatory (1918) | ||
| + | | description=''Rosa canina'' ... is distinguished by its prickly stem and petioles, and ovate, smooth, rigid leaves. It has white or pale red flowers, having usually five obcordate fragrant petals. The fruit consists of a fleshy, hollow receptacle, bearing on its inner surface a number of hairy achenes. The ripe fruit, which is usually employed in the fresh condition, is ovoid, smooth, shiny and of a reddish color. The summit is crowned with 5-calyx teeth.}} | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Microscopic Characteristics= | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Media2 |cat=Microscopy | source=Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories | ||
| companyimage= AP-LOGO-Laboratories Crop - Copy.jpg | | companyimage= AP-LOGO-Laboratories Crop - Copy.jpg | ||
| − | | companyURL=http://www. | + | | companyURL=http://www.alkemist.com |
| mainimage=Rosa canina - Alkemist Laboratories.jpg | | mainimage=Rosa canina - Alkemist Laboratories.jpg | ||
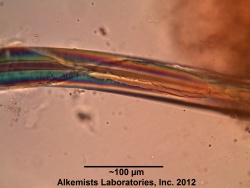
| caption1=Fragment of a unicellular thick walled trichome seen under polarized light observed at 400x with Acidified Chloral Hydrate Glycerol Solution. | | caption1=Fragment of a unicellular thick walled trichome seen under polarized light observed at 400x with Acidified Chloral Hydrate Glycerol Solution. | ||
| − | | | + | | source2=Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories |
| + | | companyimage2= AP-LOGO-Laboratories Crop - Copy.jpg | ||
| + | | companyURL2=http://www.alkemist.com | ||
| image2=Rosa canina-1 - Alkemist Laboratories.jpg | | image2=Rosa canina-1 - Alkemist Laboratories.jpg | ||
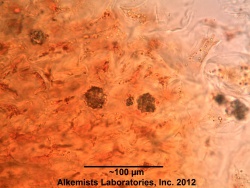
| caption2=Rosette of calcium oxalate observed at 400x with Acidified Chloral Hydrate Glycerol Solution. | | caption2=Rosette of calcium oxalate observed at 400x with Acidified Chloral Hydrate Glycerol Solution. | ||
| Line 14: | Line 52: | ||
| }} | | }} | ||
| − | = | + | =High Performance Thin Layer Chromatographic Identification= |
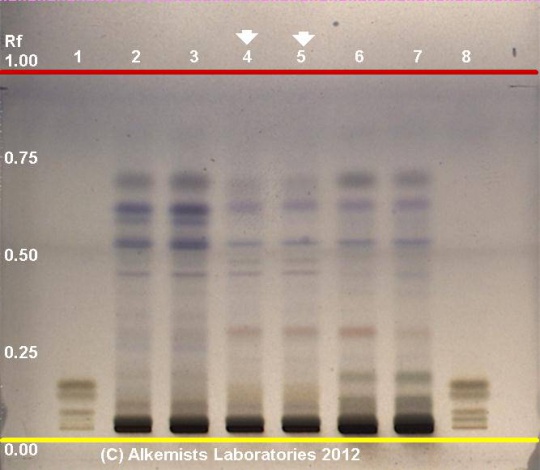
{{HPTLC | source=Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories | {{HPTLC | source=Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories | ||
| description=Rosehips (fruit) (''Rosa canina'') | | description=Rosehips (fruit) (''Rosa canina'') | ||
| Line 41: | Line 79: | ||
| − | = | + | =Supplementary Information= |
| − | + | =Sources= | |
| + | <references /> | ||
Latest revision as of 15:03, 7 April 2015
Contents |
Nomenclature
Rosa canina L. Rosaceae
Standardized common name (English): dog rose
Botanical Voucher Specimen
|
|
Organoleptic Characteristics
|
Macroscopic Characteristics
|
Microscopic Characteristics
 |
 |
|
|
|
High Performance Thin Layer Chromatographic Identification
|
Rosehips (fruit) (Rosa canina) Lane Assignments Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample):
Reference materials used here have been authenticated by macroscopic, microscopic &/or TLC studies according to the reference source cited below held at Alkemists Laboratories, Costa Mesa, CA. Stationary Phase Silica gel 60, F254, 10 x 10 cm HPTLC plates Mobile Phase toluene: acetone: HCOOH [6/3/1] Sample Preparation Method 0.3g+3mL 70% grain EtOH sonicate/heat @~50° C ~ 1/2 hr Detection Method Vanillin/H2SO4 Reagent -> 110° C 5 min -> visible light Reference see Adapted from European Pharmacopoeia 5.0 2005
|
Supplementary Information
Sources
- ↑ MOBOT, Tropicos.org http://www.tropicos.org/Image/100179847
- ↑ United States Dispensatory (1918)
- ↑ United States Dispensatory (1918)
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com