Plantago ovata (seed husk)
m |
|||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
=Microscopic Entries= | =Microscopic Entries= | ||
| − | {{Microscopy | source=Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories | + | {{Microscopy | source=Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories |
| companyimage= AP-LOGO-Laboratories Crop - Copy.jpg | | companyimage= AP-LOGO-Laboratories Crop - Copy.jpg | ||
| companyURL=http://www.Alkemist.com | | companyURL=http://www.Alkemist.com | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
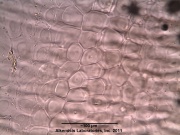
| caption2=Parenchyma cells seen under polarized light observed at 400x with Acidified Chloral Hydrate Glycerol Solution. | | caption2=Parenchyma cells seen under polarized light observed at 400x with Acidified Chloral Hydrate Glycerol Solution. | ||
| characteristics=cellular structures identified in this botanical specimen are the epidermal cells of the husks in surface view containing mucilage and the parenchyma cells seen under polarized light when observed at 400x with Acidified Chloral Hydrate Glycerol Solution. | | characteristics=cellular structures identified in this botanical specimen are the epidermal cells of the husks in surface view containing mucilage and the parenchyma cells seen under polarized light when observed at 400x with Acidified Chloral Hydrate Glycerol Solution. | ||
| + | | reference=British Pharmacopoeia, 2011 | ||
| }} | | }} | ||
Revision as of 05:09, 3 October 2012
Contents |
Introduction
Introduction from Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plantago_ovata and http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Psyllium_seed_husks, retrieved 02/27/2012).
Plantago ovata (Desert Indianwheat, Blond Psyllium; syn. Plantago brunnea Morris, Plantago fastigiata Morris, Plantago gooddingii A. Nels. & Kennedy, Plantago insularis Eastw., Plantago insularis Eastw. var. fastigiata (Morris) Jepson, Plantago insularis Eastw. var. scariosa (Morris) Jepson, Plantago minima A. Cunningham) is a medicinal plant native to Western Asia and Southern Asia.
It is a common source of psyllium seed husks, a material used as dietary fiber.
The plant can be found growing wild in the southwestern United States, where it is an introduced species.
Psyllium seed husks also known as ispaghula, isabgol, or psyllium, are portions of the seeds of the plant Plantago ovata, (genus Plantago), a native of India. They are hygroscopic (that is they absorb water expanding and become mucilaginous.
Psyllium seed husk are indigestible and are a source of soluble dietary fiber.
The quoted text in this section was licensed for use under the Creative Commons ShareAlike License, version 3.0: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Macroscopic Entries
Microscopic Entries
|
HPTLC Entries
Other Points of Interest
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found